Eshelby
This example demonstrates the Mechanics solver using the Eshelby inclusion problem. The example primarily tests the following Alamo capabilities
In 2D, the sigma_xx solution is:
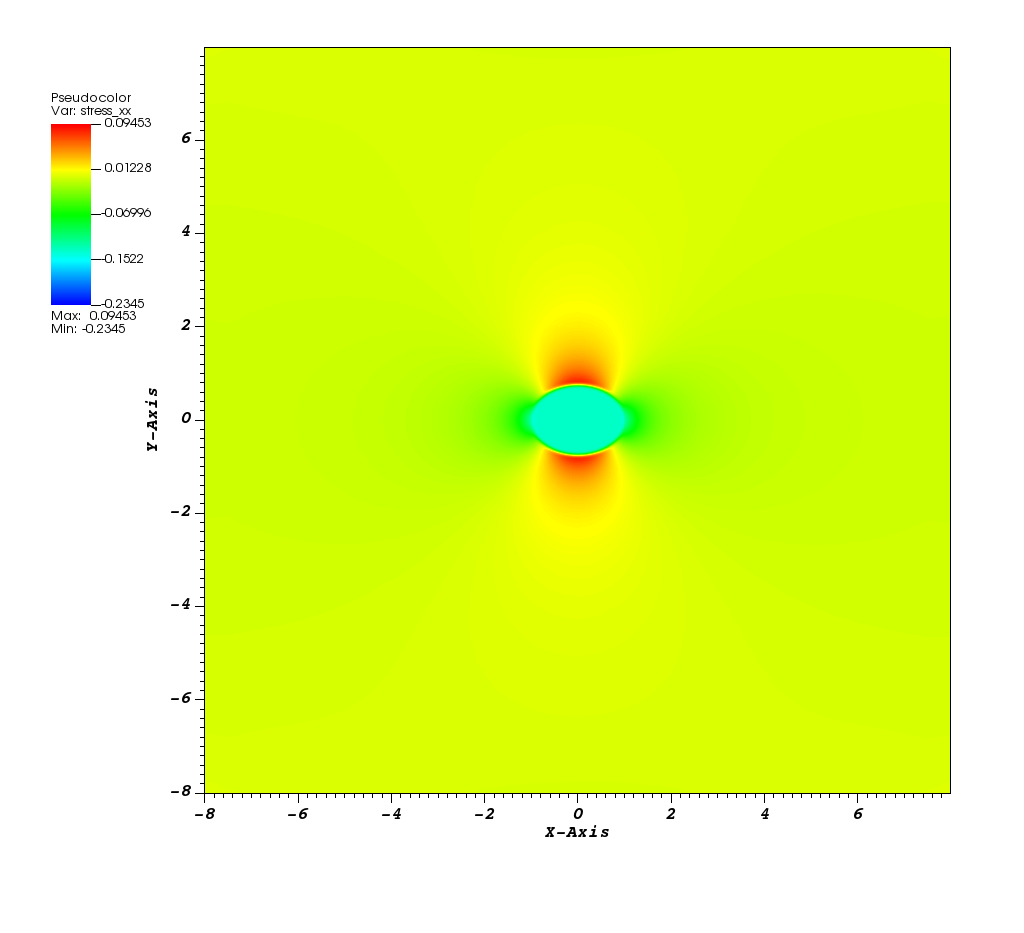
In 3D, the solution is tested against the exact solution derived using Eshelby inclusion theory. For additional background see Runnels et al: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.110065
2D-serial-5levels
Two-dimensional |
|
Serial |
|
Not validated |
|
./bin/mechanics-2d-g++ tests/Eshelby/input
|
2D-serial-5levels-coverage
Two-dimensional |
|
Serial |
|
Not validated |
|
./bin/mechanics-2d-g++ tests/Eshelby/input amr.max_level="3"
|
3D-serial-4levels
Three-dimensional |
|
Serial |
|
Validated using check script |
|
16.10s (beaker) 11.36s (statler) 22.75s (github) |
|
./bin/mechanics-3d-g++ tests/Eshelby/input amr.max_level="4"
|
3D-parallel-5levels
Three-dimensional |
|
Parallel (4 procs) |
|
Validated using check script |
|
24.66s (beaker) 18.76s (statler) |
|
mpiexec -np 4 ./bin/mechanics-3d-g++ tests/Eshelby/input
|
Input file (../../tests/Eshelby/input)
#@ [2D-serial-5levels]
#@ exe = mechanics
#@ dim = 2
#@ nprocs = 1
#@ check = false
#@
#@ [2D-serial-5levels-coverage]
#@ exe = mechanics
#@ dim = 2
#@ nprocs = 1
#@ check = false
#@ coverage = true
#@ args=amr.max_level=3
#@
#@ [3D-serial-4levels]
#@ exe = mechanics
#@ dim = 3
#@ nprocs = 1
#@ args = amr.max_level=4
#@ benchmark-beaker = 16.10
#@ benchmark-statler = 11.36
#@ benchmark-github = 22.75
#@
#@ [3D-parallel-5levels]
#@ exe = mechanics
#@ dim = 3
#@ nprocs = 4
#@ benchmark-beaker = 24.66
#@ benchmark-statler = 18.76
alamo.program = mechanics
alamo.program.mechanics.model = affine.isotropic
plot_file = tests/Eshelby/output
# this is not a time integration, so do
# exactly one timestep and then quit
timestep = 0.1
stop_time = 0.1
# amr parameters
amr.plot_int = 1
amr.max_level = 5
amr.n_cell = 32 32 32
amr.blocking_factor = 8
amr.regrid_int = 1
amr.grid_eff = 1.0
amr.cell.all = 1
# geometry
geometry.prob_lo = -8 -8 -8
geometry.prob_hi = 8 8 8
geometry.is_periodic = 0 0 0
# ellipse configuration
ic.type = ellipse
ic.ellipse.a = 1.0 0.75 0.5 # ellipse radii
ic.ellipse.x0 = 0 0 0 # location of ellipse center
ic.ellipse.eps = 0.1 # diffuse boundary
# elastic moduli
nmodels = 2
model1.E = 210
model1.nu = 0.3
model1.F0 = 0.001 0 0 0 0.001 0 0 0 0.001 # eigenstrain
model2.E = 210
model2.nu = 0.3
model2.F0 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 # eigenstrain
solver.verbose = 3
solver.nriters = 1
solver.max_iter = 20
bc.type = constant